This article was originally published on The Conversation, which features includes relevant and informed articles, written by researchers and academics in their areas of expertise and edited by experienced journalists.
Jean-Philippe Pignol is professor and chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology at Dalhousie University. Nienke Hoekstra is a PhD student in Radiotherapy, Erasmus MC, Netherlands and Dalhousie University.
Women who have been lucky enough to survive breast cancer may face increased risk of lung cancers, according to a new study in Radiotherapy and Oncology. The study shows how this can be prevented — limiting the radiation dose to a lung, using a treatment which targets only a small part of the breast.
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women, with more than 266,000 new cases diagnosed in 2018 in the United States.
Thanks to the widespread use of screening mammography, most women are now diagnosed at an early stage — meaning that the cancer has only grown in the breast and not spread under the armpit or to distant organs. These individuals have a good prognosis with only a 1.3 per cent risk of dying of cancer recurrence after five years.
Treatment currently involves a limited breast surgery followed by multiple daily radiation treatments targeting the whole breast. However, despite being cautiously delivered, a small amount of radiation can spill into the lung.
Using a complex predictive model called the Biologic Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) VII, and by testing multiple radiation techniques on a realistic model of a breast cancer patient, the study by PhD student Nienke Hoekstra shows that the risk of lung cancer slowly increases five to 10 years after a breast radiation treatment. It reaches three per cent of surviving patients after more than 30 years.
A small part of the breast
This risk of lung cancer is a real concern for young patients diagnosed with early stage breast cancers — for example, a ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), which is a form of non-invasive cancer and hence a very highly curable disease. These patients have the chance of living long enough to experience this scary treatment side-effect.
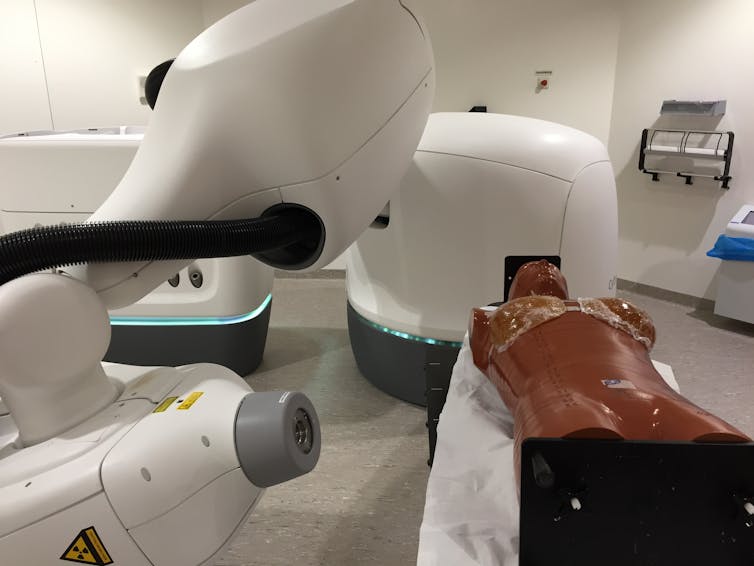
The good news is that risk is not the same for all radiotherapy techniques. The study shows that a new form of radiotherapy for early-stage breast cancers — called accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) — dramatically reduces this risk.
APBI delivers the radiation treatment to only a small portion of the breast. It focuses on the cavity left after the surgery, where there is risk that cancer cells may remain.
There are multiple advantages to APBI, including the delivery of treatment in just five days. And the study found it results in much lower radiation exposure to body organs, including the lungs, than conventional treatments.
APBI is a technique on the rise. This study adds to the growing amount of evidence that it should be the preferred technique for women with very low-risk breast cancer.
But not all patients will benefit from APBI. Some need more complex and extensive radiotherapy to save their lives. Patients should be encouraged to discuss this with their radiation oncologist.
Tiny radioactive seeds
Among APBI techniques tested, “brachytherapy” — a form of radiotherapy where radioactive material is implanted inside the surgical cavity — appears to be the safest.
A particular form of brachytherapy developed in Canada, called “permanent breast seed implant,” is the one with the lowest risk of secondary lung cancer.
This technique, which is also used to treat prostate cancer, involves the permanent implantation of tiny radioactive seeds, the size of a grain of rice, during a one-hour procedure performed under light sedation. Patients are discharged the same day.
The radiation emitted by the radioactive seeds is so weak that it is absorbed within a few millimetres and hence rarely reaches other organs.
![]() The good news is that there is still lots of room for improvement — for example, using a robotic delivery of radiation from all angles around the breast to better avoid the lung. This is the focus of ongoing research.
The good news is that there is still lots of room for improvement — for example, using a robotic delivery of radiation from all angles around the breast to better avoid the lung. This is the focus of ongoing research.
Read the original article on The Conversation.
Dalhousie University is a founding partner of The Conversation Canada, a new-to-Canada online media outlet providing independent, high-quality explanatory journalism. Originally established in Australia in 2011, it has had more than 85 commissioning editors and 30,000-plus academics register as contributors. A full list of articles written by Dalhousie academics can be found on the Conversation Canada website.

