Donna J. Bird

M. Sc. Thesis
The Depositional Environments of the Late Carboniferous, Coal-Bearing Sydney Mines Formation at Point Aconi, Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia
(PDF - Mb)
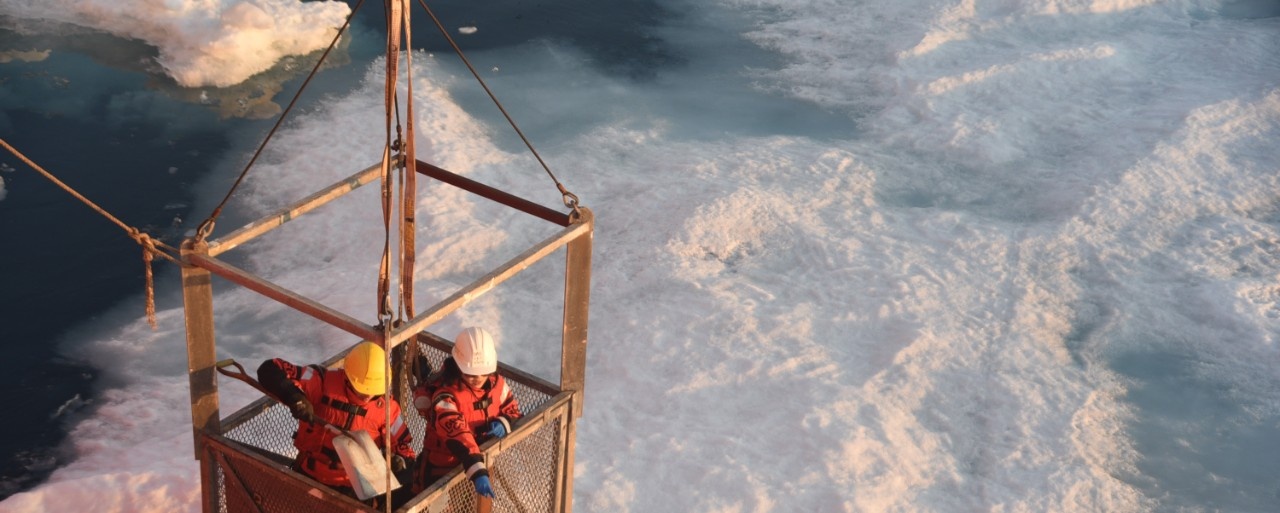
The Sydney Mines Formation at Point Aconi, Cape Breton Island, is the youngest onshore exposure of the Late Carboniferous, coal-bearing, Sydney Basin. The purpose of this study is to measure and document the geological characteristics of the stratigraphic column along the eastern coast of the Bras d'Or Inlet and to interpret the depositional environments of the rocks. Collected field data were combined with drill log information to characterize the regional depositional setting.
Individual mappable lithological units are interpreted to have been deposited in terrestrial and coastal marine environments. Meandering-fluvial channels up to 12.5m deep drained across terrestrial and coastal marine settings. The sedimentary bodies deposited by the fluvial channels include channel-shaped, fining-up sandstone bodies and overbank sandstone and mudstone. In the terrestrial setting, some of the grey mudstones were oxidized to red. In the coastal marine settings, peat growth accumulated to be preserved as coal seams.
The examined Sydney Mines Formation strata consist of ten cyclothems ranging in thickness from 40 to over 70 m. Each cyclothem is divided into eight intervals and each interval consists of a distinctive, laterally extensive assemblage of sedimentary bodies. The lower three assemblages are interpreted to be terrestrial and the upper five are interpreted to be coastal marine.
Defined cyclothems are interpreted to be regressive/transgressive couplets. The regressions and transgressions may be synchronous with the regressive/transgressive cyclothems of Europe and the United States, and the regressions and transgressions in all three locations are considered to have been controlled by sea-level fluctuation. Sea level fluctuation was probably driven by the buildup and melting of Gondwanan glaciers as multiple continental glacial expansions and recessions occurred in the southern hemisphere during the time of deposition of the Sydney Mines Formation.
Keywords:
Pages:
Supervisor: Martin Gibling