Cannabinoids & Arthritis Pain
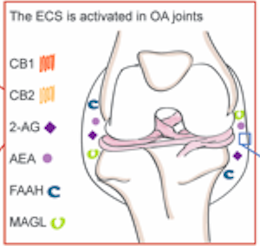
Medical cannabis has been proposed to be beneficial for the management of arthritis symptoms. The McDougall lab was the first to show that cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) are located on nerves in the joint and activation of CB1 can reduce osteoarthritis pain. We further discovered that CB1 agonists can reduce neurogenic inflammation.
Joints can also produce compounds with cannabis-like properties. These endocannabinoids are rapidly broken down by enzymes (fatty acid amide hydrolase, monoacylglyerol lipase) thereby limiting their physiological effectiveness. We found that inhibitors of these enzymes introduced locally into the joint can reduce pain and inflammation.
Relevant Publications:
Combatting joint pain and inflammation by dual inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase and cyclooxygenase-2 in a rat model of osteoarthritis. HP Philpott & JJ McDougall. Arthritis Research & Therapy. (2020)
Cannabis and joints: scientific evidence for the alleviation of osteoarthritis pain by cannabinoids. MS O'Brien & JJ McDougall. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. (2018)
Attenuation of early phase inflammation by cannabidiol prevents pain and nerve damage in rat osteoarthritis. HP Philpott, MS O'Brien & JJ McDougall. Pain. (2017)
Early blockade of joint inflammation with a fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor decreases end-stage osteoarthritis pain and peripheral neuropathy in mice. JJ McDougall, MM Muley, HP Philpott, AR Reid & E Krustev. Arthritis Research & Therapy. (2017)
Endocannabinoids inhibit neurogenic inflammation in murine joints by a non-canonical cannabinoid receptor mechanism. E Krustev, MM Muley & JJ McDougall. Neuropeptides. (2017)
Tapping into the endocannabinoid system to ameliorate acute inflammatory flares and associated pain in mouse knee joints. E Krustev, AR Reid, JJ McDougall. Arthritis Research & Therapy. (2014)
The abnormal cannabidiol analogue O-1602 reduces nociception in a rat model of acute arthritis via the putative cannabinoid receptor GPR55. N Schuelert & JJ McDougall. Neuroscience Letters. (2011)
Local application of the endocannabinoid hydrolysis inhibitor URB597 reduces nociception in spontaneous and chemically induced models of osteoarthritis. N Schuelert, MP Johnson, JL Oskins, K Jassal, MB Chambers & JJ McDougall. Pain. (2011)
Paradoxical effects of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist GW405833 on rat osteoarthritic knee joint pain. N Schuelert, C Zhang, AJ Mogg, ML Broad, DL Hepburn, ES Nisenbaum, MP Johnson & JJ McDougall. Osteoarthritis & Cartilage. (2010)
Cannabinoid-mediated antinociception is enhanced in rat osteoarthritic knees. N Schuelert & JJ McDougall. Arthritis & Rheumatism. (2008)
